cheese hazard analysis
17 of 243 noncontact surfaces Menendez. Cheese is generally considered a safe and nutritious food but foodborne illnesses linked to cheese consumption have occurred in many countries.
Can some one post me a link or share a document for haccp plan in cheese manufacturing.

. To set up a specific HACCP plan for this small-scale cheese plant. Whereas for dairy cheese there is 100 years of food safety science. Carbon dioxide occurs naturally in milk but most of it is lost in the course of processing.
It is generally recognized that the production of cheeses with desirable organoleptic char-. Any component of an organization is considered as a cheese slice of this model. Critical limits were estab-.
Thanx for the link before but i cant find what im looking for. When the shape parameter varies between 2 and 5 the corresponding distribution is nearly bell-shaped. The traditional inspection and quality procedure in order to prevent the hazards in the cheese product.
To evaluate the current methods of analysis on hazards that appear during the processing and control procedures used in the plant. The key determinant for the safety. Several microorganisms like spoilage and pathogens such as.
Here well identify hazards relevant to cheese making in general terms. Adding carbon dioxide by artificial means lowers the pH of the milk. Identification of the risk factors associated with cheese production to implement the hazard analysis and critical control points HACCP system on cheese farms The purpose of this paper was to evaluate by statistical analyses risk factors on cheese farms that can influence the microbial contamination of their products.
The tool identifies measurable parameters and provides templates to monitor and record variation to help cheesemakers understand how changes in raw materials and processes impact the sensory characteristics consistency and quality of their cheese. Use of cheese as a raw material in the manufacturing food process EDA has indicated to the European. HAZARDS IN RAW MILK CHEESES.
2 all operated food safety management HACCP. Remove at least 1-inch around and below the mold spot. In this study a methodological.
The Swiss cheese model is a theoretical assumption that is used in risk management risk analysis and risk prevention before any accident. All made fresh cheese. Keep the knife out of the mold itself so it will not contaminate other parts of the cheese.
Due to its freshness low humidity and lower level of salt this cheese is in higher risk of contamination than other traditionally produced ones. A hazard analysis was conducted to identify hazards that may occur in the product cycle Critical Control Points CCPs were determined to control the identi-fied hazards. This is the area that has the least science support for these products.
3 they produced between 10 and 1000 L of milk per day. Glad to found this site. Staphylococcus aureuswas the most frequent pathogen associated with cheeses from raw or unspecified milk in food-borne disease.
The concept of Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points HACCP is a preventive structured systematic and documented approach to ensure food safety Bu-chanan 1990 Motarjemi Kaferstein Moy Miyagawa Miyagishima 1996. Raw milk can directly contaminate cheese with pathogenic organisms if it is not pasteurized See Section 94. CCP signs were then posted on the factory floor.
The hazard analysis critical control point system HACCP is a widely used tool in the food industry and recommended in the water safety plans WSP approach. This looked a bit more. It is also known that actively growing cultures can inhibit the growth of pathogens.
Microbial hazards occur most frequently but chemical hazards such as antibiotics and physical hazards such as metal contamination must also be considered. HACCP is a management tool to assess food safety hazards identify Critical Control Points CCPs where control can be applied effectively and control the control measures linked to the CCP. Mold requires oxygen to grow so tightly rewrap the remaining cheese.
Management resource allocation efficient safety program operational support all are considered as a part of the cheese. Weibull hazard analysis plot for cottage cheese stored at 4C. Several microbial risk assessments related to Listeria monocytogenes Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli infections causing cheese-related foodborne illnesses have been conducted.
Line a represents the shape parameter line. 1 they were authorized by the Canary Health Service of The Autonomous Government of the Canaries to produce and sell cheese. If the block of cheese is large and molding is not extensive remove the mold to save the remaining cheese.
Brazil two cheese plants 13 10 Barancelli 2011. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points as guidance when the HACCP team establishes the plant specific GHP Good Hygienic Practice and raw material and product specific HACCP system. Carbon dioxide CO 2 Addition of CO 2 is a method of improving the quality of cheese milk as the carbon dioxide acts as an inhibitor.
Axis that is parallel to the data line. Hazard analysis cheesepng 6725KB 2 downloads. Therefore HACCP analysis of this product is important issues for public health.
HACCP plan for cheese manufacturing - posted in HACCP - Food Products Ingredients. Further analysis was undertaken to determine if it was possible to apply the findings of the risk assessments to other cheeses which lie within the same moisture category. Keep in mind that traditional cheeses often have pH values between 46-52.
Local cheese processing results in public or consumers health hazard due to the presence of pathogenic bacteria mold and yeast. Line b represents lhc data line. This intersecting value is then the shape parameter.
In a recent study on Monte Veronese cheese an Italian PDO semi- hard cheese made with raw milk Staphylococcus aureusnumbers in cheese were higher than the104CFU g-1limit in 78 of samples 1. 7 28 of non food contact surfaces in cheese plants. A document resulting from the hazard analysis that specifies how.
HACCP Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point. This cheese is a kind of fresh and soft cheese which is sold before ripening and is a popular type of cheese in Iran. 11 of noncontact surfaces in eight NJ artisan cheese factories.
The 39 cheese farms that participated in this study fulfilled the following requirements.

Pdf Hazard Analysis Of Cheese Provided For Consumers In Hawassa Ethiopia

Pdf Implementation Of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point To Feta And Manouri Cheese Production Lines Semantic Scholar

Hazard Analysis Of Cheese Processing Steps Download Table

Critical Control Points In Haccp System Set Up In Cream Cheese Production Download Table

Hazard Analysis Of Cheese Processing Steps Download Table

A Swiss Cheese Model For Reducing Biases In User Research By Biswajeet Das Ux Collective

Determinants Of Implementation Of Hazard Analysis And Critical Control Point Project In Four Selected Gouda Cheese Processing Firms In Rwanda Semantic Scholar
Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment For Consumption Of Paneer Case Study Qmrawiki

Critical Control Points In Haccp System Set Up In Cream Cheese Production Download Table

Pdf Implementation Of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point To Feta And Manouri Cheese Production Lines Semantic Scholar

Haccp Plan For Pasteurized Milk Download Table
Aie Aie S Safety Engineering Team Discuss Major Accident Hazards And Bowtie Analysis

Pdf Implementation Of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point To Feta And Manouri Cheese Production Lines Semantic Scholar

What S Swiss Cheese Got To Do With Root Cause Analysis
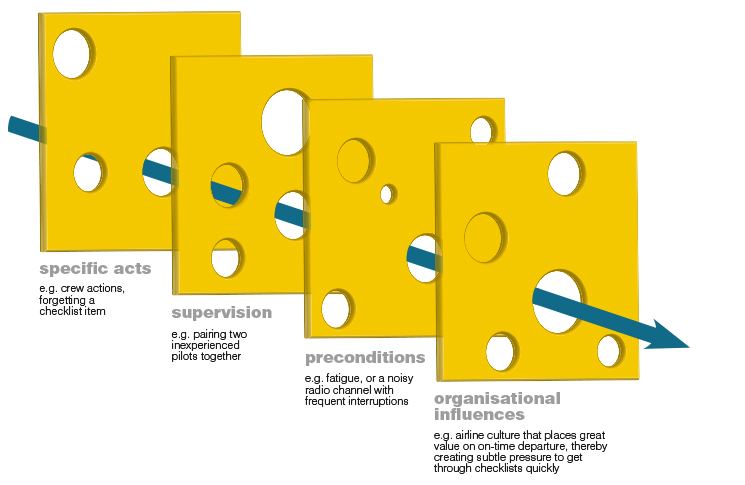
Safety In Mind Swiss Cheese And Bowties Flight Safety Australia



Comments
Post a Comment